Abstract
Background: High-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (SCT) is the current standard of care for myeloma patients for attaining deeper responses. Generic melphalan formulations that were used for more than half a century were susceptible to several challenges (marginal solubility, limited chemical stability after reconstitution and prone for hydrolysis, requirement of propylene glycol as a co-solvent, etc). Evomela™, a Captisol®-stabilized propylene glycol-free melphalan preparation recently obtained FDA indication for use as a high-dose conditioning treatment prior to SCT in patients with myeloma. However, no comparative data relative to conventional melphalan exists. The objective of our study was to evaluate if Evomela™, a more stable compound, can potentially be delivered at the intended dose and deliver higher response rates relative to melphalan. We also reviewed the safety of Evomela™ compared to the generic formulation in this retrospective analysis.
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis comparing 2 sequential cohorts of myeloma patients that underwent autotransplant at a single institution. Our institution switched to Evomela™ on September 15th 2016. Approximately 201 patients received a single autotransplant with Evomela™ from September 15th 2016 until September 14th 2017. The control group (193 patients) received conventional melphalan from September 15th 2015 until September 14th 2016. Both Evomela™ and the conventional melphalan were administered on the same day of transplant with the same amount of infusion time. Patient characteristics, toxicity and responses at day 100 were collected and compared between the 2 groups. Fischer's exact and Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel tests were used to compare responses and toxicities.
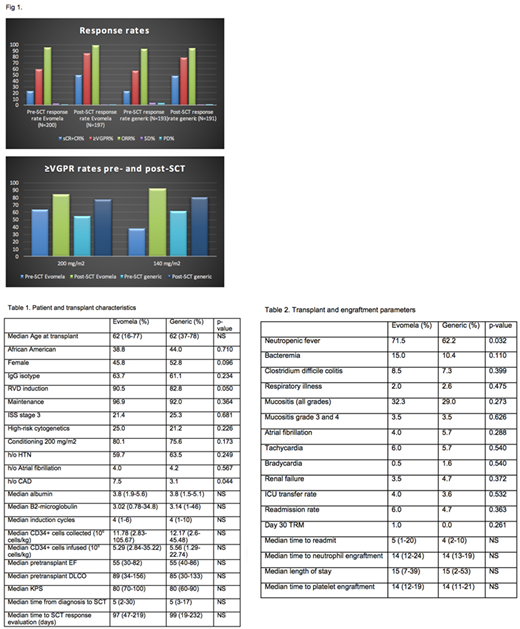
Results: Median age of the patients is 62 years (range 16-78). Patient and transplant characteristics were summarized in Table 1. Both of the groups are balanced, except for 2 variables. The Evomela™ group had higher rates of patients with CAD and 8% more patients received RVD induction therapy. All of the pre-transplant parameters, conditioning regimens and median CD34+ cells infused were similar. The post-SCT ≥VGPR rate was significantly higher for Evomela™ relative to melphalan (85.3% vs 78%, p=0.043), especially when the ≥VGPR rates prior to SCT were similar across the 2 groups (58.5% vs 56.5%, p=0.381), Fig 1. While the difference is seen for both 200 mg/m2 (63.8% vs 54.8%) as well as 140 mg/m2 (91.9% vs 80.4%), the ∆ change (pre-SCT VGPR to post-SCT VGPR) is highly significant among patients receiving Evomela™ 140 mg/m2 vs melphalan (37.5% to 91.9% for ∆ 54.4% vs 61.7% to 80.4% for ∆ 18.7%, p<0.001). Higher rates of neutropenic fevers were seen in the Evomela™ group (p=0.032) but the safety profile, day 30 transplant related mortality, readmission rates, ICU transfers and cardiac complications were similar to melphalan, as outlined in Table 2.
Conclusions: These results suggest that by using Evomela™ the intended dose of the alkylating agent is delivered when compared to the conventional melphalan formula. Considering the similar complication rates and safety profile while obtaining higher and deeper response rates supports the use of Evomela™.
Kaufman:BMS: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Other: data monitoring committee; Janssen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy. Hofmeister:Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Adaptive biotechnologies: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Waller:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Other: Travel Expenses, EHA, Research Funding; Kalytera: Consultancy; Cambium Medical Technologies: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Celldex: Research Funding. Heffner:Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Lonial:Amgen: Research Funding. Nooka:GSK: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive technologies: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal